The information society will remain an empty concept if one talks solely about technology, network and access issues. Considering the general use or impact of the information is meaningless, unless we carry the messages, which those can translate. The World Summit Award (WSA), the global initiative to select and promote the world’s best e-Content, looks into this aspect of technology for which, it is a global hub for everyone today. As of today, 168 countries are actively involved in WSA. By selecting, presenting and promoting the best products from all over the world in that field, it makes a contribution to bridging the Digital Divide and narrowing the Content Gap. The World Summit Award will hold the Grand Jury for the selection of the World’s Best in e-Content in Croatia in 2007.
Connecting this global platform to the fact that India is one of the poor countries in exposing its content using digital media, and its information assets are still weekly represented, a parallel process, Manthan award for best e-content practices in the framework of WSA started recognising the Indian ventures which speak less of the technology and more of the usage for final delivery. The best econtent practices in India for 2006 recognised by Manthan Awards is going to be announced this August. Such initiatives recognising the contents will open doors for global recognition and support to the local initiatives, understanding the fact that e-content will enable every citizen to become self-reliant on the basis of information prowess .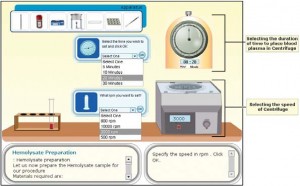
Designing Virtual Labs
Hilmi Quraishi [HILMI@ZMQ.IM], ZMQ Software Systems, India
The advancement in educational technology and tools have unleashed the opportunity to take e-learning and e-content to the next level by delivering complex concepts and scientific processes, which are often not easily rendered in words, into virtual laboratories and simulated systems. Theoretical and
scientific concepts are converted into dynamic, engaging and effective content using simulations. Instructionally, simulation makes a process easier to understand, increases retention of information, and helps build skills and competencies by letting learners understand complex scientific processes. The instructional design strategy to develop virtual laboratory combines learning theories, e-learning experience, technological innovation, and visualisation.
Instructional Strategies
Learning theories have significant bearing on instructional design, as there is a logical development from learning to instruction. Instructional design optimises learning outcomes while learning theories are the backbone of any instructional design. The three basic schools of learning theories, namely Behaviourism (changes in behaviour as the outcome of learning), Cognitivism (learning occurs when learners add new concepts and ideas to the cognitive structure) and Constructivism (learners construct knowledge for themselves) have their own implications for instructional design.
Key Implications
Learning theories and models have different implications for instructional design. While designing instructional strategies, inspirations must be taken from variety of instructional theories and models. For learners, some of the key implications of virtual laboratories and scientific based simulated systems are: Quicker and Easier Learning, Mastery of Content, Problem Solving Approach, Provide Feedback to einforce Performance, Participation in Learning, Adaptive Learning Approach, Promote Scientific Thinking, Project based Learning, Situational Learning Environment, Address Multiple Learning Styles
A Virtual Experience
With the spread of Internet access, it is now possible to offer students virtual laboratories through the World Wide Web. The idea of developing a virtual laboratory is to train the students as many number of times as possible. The students are exposed to the real laboratory, where they go through the experiment once. Virtual laboratory is distinguished from a real or a traditional laboratory. However, virtual laboratory is not viewed as a replacement for a real laboratory. nstead, virtual laboratories are possible extensions to real laboratories and open new opportunities not realisable entirely within a real laboratory at an affordable cost.
A case study
Virtual laboratory Electrophoresis e- Lab was designed to train medical students and technical trainees in clinical laboratory on Electrophoresis experiment. Electrophoresis is an analytical method frequently used in molecular biology and medicine, and is applied for the separation and characterization of sub-cellular sized particles. The objective of the experiment is to observe different band patterns and interpret results of various samples of normal and clinical conditions. The main idea of the virtual lab is to create a real lab environment using scripted model with controlled animations. It is not just demonstrating a process using animations, but rather developing programmatically controlled scripted simulations using animated components. Some of the labs can be viewed at the link: http://www. zmqsoft.com/elearning/home.htm An example of virtual lab is presented here. The simulator also tracks the performance of a user. It monitors different steps taken during the course of experimentation, number of attempts taken to complete it successfully, and provide results of all experimental input values with feedback. The idea is to create an environment for learner, where the learner practically experiments the processes by changing different input values and parameters.
Key Components
Besides developing a simulated learning environment, the e-Lab is also supported by other different learning components to give a complete learning solution to the learners. The key components are- Pre-Test: It prepares learner for the next stage of learning by stimulating the recall of prerequisite nowledge. Pre-test is an essential for creating adaptive learning environment.
Theory: The content theory provides with detailed description and explanation of concepts, rules and principles for clearer understanding. It comprsies of different case studies, examples, non-examples and simulated diagrams for quicker understanding. Interactive Exercise: Various practice exercises like multiple choice questions, single choice questions,. drag-and-drop, match-the-following, filling-in-the-blanks etc; allow the learner to practice opportunities to aid in retention of information and creation of knowledge. Feedback: The feedback encourages the learner to improve thinking and understanding of the problem. The feedback for an incorrect response should provide the correct answer for the learner in an effort to improve future performance. Post Test: It is used to assess the performance of learner and new knowledge that has been integrated correctly. Often, educational technologists also use post-test values to make corrective measures in their learning environment. Other Components: Other important components of a complete virtual learning environment are glossary, FAQs, help, know-more etc. to provide complete support during process of learning. Virtual labs have opened up new opportunities at an affordable cost. Experiment-oriented problems can be offered without the overhead incurred to experimentation, problem solving and data gathering