 Research showed that most people have mobile phones in Malaysia no matter where they are and thus able to reach out to people in the remote area. There are more than one and a half billion mobile phones in operation around the world, and a large percentage of them are in the hands of students and working adults. LTT Global Communications as educators embrace the potential of mobile technology and explores the possibilities to bring educational content direct to end-users anywhere anytime thus teaching innovatively and powerfully for learners of any age with speed, power and effectiveness. SMS-ME-ENGLISH is one such innovation explored making English learning EASY, FUN, FAST and PRACTICAL!
Research showed that most people have mobile phones in Malaysia no matter where they are and thus able to reach out to people in the remote area. There are more than one and a half billion mobile phones in operation around the world, and a large percentage of them are in the hands of students and working adults. LTT Global Communications as educators embrace the potential of mobile technology and explores the possibilities to bring educational content direct to end-users anywhere anytime thus teaching innovatively and powerfully for learners of any age with speed, power and effectiveness. SMS-ME-ENGLISH is one such innovation explored making English learning EASY, FUN, FAST and PRACTICAL!
As initiators and pioneers of mobile learning both locally in Malaysia and globally, LTT Global Communication’s business objective is to make learning easily available and affordable to all. LTT Global Communications is a company under the Technopreneur Development Flagship of the Multimedia Development Corporation, an initiative by the government of Malaysia in Cyberjaya. It represents a few companies in the Asia Pacific Region for contents on the mobile platform. Co-founded by Wemel Cumavoo and Rani Wemel, the company bears the joint vision of bringing mobile learning to all using mobile devices such as a Palm Pilot or mobile phone, to support learning and performance on the job.
LTT Global Communications started with the roll out of SMS-ME-ENGLISH ver1.0, an innovative programme and an affordable way to learn a language easily. SMS-ME-ENGLISH is packaged every weekday and send out via SMS. It is designed in Dwi Bahasa (dual language) to help one master the English language, Bahasa Malaysia or BOTH languages! SMS-ME-ENGLISH was officially launched in August 2004 by Dato’ S.Veerasingam, Deputy Minister of Domestic Trade and Consumer Affairs in Malaysia. This launch witnessed the signing ceremony between LTT Global Communications and Maybank, Bumiputra-Commerce Bank , RHB Bank and Bank Islam appointment as the collection agent for SMS-ME-ENGLISH programme via Internet banking.
 Some success stories
Some success stories
A strategic partnership with Advanced Manufacturing Institute (AMI) of MIGHT METEOR Advance Manufacturing Sdn Bhd (MMAM), in collaboration with
LTT Global is among the ‘Preferred Learning Partners’ of Blue Hyppo (TMNet Internet Service Provider – a subsidiary of Telekom Malaysia). Soh Chin Yit a subscriber to its service through TMNet, scored A1 in his English 119, SPM 2005 (equivalent to ‘O’Levels). Also in the photo (Right) Wimel Cumavoo, the co-founder of LTT Global Communications
the Economic Planning Unit (EPU), Prime Minister’s Department in providing technology enhanced learning experience for unemployed and fresh graduates. Customised English programme sent to their mobiles in line with their coursework they are attending at Advanced Manufacturing Institute.
Shared experiences with BECTA, ICT Research Network (British Educational, Communications and Technology Agency), about using SMS as a learning platform.
SMS-ME-ENGLISH today is further enhanced with (24/7) web assisted learning. All participants are to be awarded a Certificate of Completion issued by the Institute of Professional Development of the Open University Malaysia in collaboration with LTT Global Communications Sdn Bhd after successfully completing the 1 year programme as per the study guide. Today, Pos Malaysia Online and TM Net, a Telekom Malaysia subsidiary also have come aboard to provide the programme to their customer base. The partnership is consistent with the efforts of LTT Global to bring mobile learning to all.
The mobile lifestyle learning suite that the company provides is a complete suite designed to make mobile learning solution really easy. A complete learning suite is provided having full capacity from registration for courses from payment to receiving lessons all at the finger tips anywhere, anytime.
BASIC is for people who only speak Bahasa Malaysia and is designed in dwi bahasa to bring them into speaking English with ease.
Example of lesson sent to mobile: COME disebut (kam). maksud: datang, mari. contoh:1.Come to my house. 2.Come and sit with me.
INTERMEDIATE is in dwi bahasa as well but is for those who are not so confident yet about their English language, this phase helps them better understand the meaning to enable them to speak with confidence.
Example of lesson sent to mobile: COMPLEX disebut (kom-pleks). maksud: bangunan, rumit. contoh:1.Abu went to the office complex. 2.Ida has a complex decision to make.
ADVANCE level is all in English for all English speaking people at all levels to empower their language further.
Example of lesson sent to mobile: CAJOLE: kah-JOEL means: to coax or persuade, eg.: She is not very excited about the trip, but I will be able to cajoel her into coming.
The company’s mobile contents range from ‘LIVE’ games to those tailored content development covering four main areas of education, lifestyle, family and professional. It has leading courseware for all handheld devices, like hand-phone, Palm, Pocket PC/PDA made available on SMS/ MMS/ WAP/ GPRS(2G-3G) platform. It has a mobile edutainment and infotainment service for users to experience interactive entertainment and games from their handheld device. The infotainment content enables businesses to market themselves while offering entertainment to their customers.
C-DAC based in Pune and Enable M, a Mumbai-based Mobile Technology company in India has jointly developed a technology for learning Indian languages through artificial intelligence, on mobile phones.
The technology named as LILA (Learn Indian Language through Artificial Intelligence), is a result of the joint efforts of both the premier organizations engaged in developing indigenous solutions in hi-tech areas. LILA provides the facility to read and listen to the sound of Devanagiri alphabet, just as it is used in Hindi. It also has the ability to understand how words are formed and pronounced in Hindi as well as a vocabulary for commonly used words and look-up Hindi-English dictionary. The Hindi sentence structure patterns are exposed with a relative English version.
To make it user friendly, there are exercises and practice sessions available for the users. The narrative sections of lesson include integrated video clips. Further, even the translation of Hindi sentences can be seen on the screen.
The mobile content for palm/ PDA/ pocket pc platform includes leading courseware in marketing, business, sales, job search, etc. used by Fortune 500 companies. The company works with the leading provider of mobile authoring, publishing, delivery and tracking solutions. The need for mobile content in the form of learning, reference, testing and and job aides to support a growing remote and field workforce which is met using the content development and publishing system (LMA) integrated with the mobile delivery and tracking system (MDTS). Organisations will have the tools and knowledge needed to launch and track mobile initiatives faster and more cost effectively than one would have ever imagined. The mobile software and hosted ASP solutions of the company give the power to design, create, edit, deploy .







 Project-based learning (PBL) via the integration of technology in science teaching is one of the contextual learning approaches that has gained much popularity and increased attention in the recent years. Project-based activities become the precursor for the advancement of Science and Technology Education (STE) in developing countries. Research findings indicate that the use of technology allows students to present their projects in an interesting and comprehensive manner. Science projects are usually triggered from simple questions or problems in various contexts. With a close guidance by the mentors, students’ project work could provide the motivating and effective contexts for the acquisition of research skills, scientific understanding, problem solving and critical/creative thinking skills. Technology, in a variety of sophisticated forms, in turn challenges the student to create many tasks in line with each individual’s knowledge and proficiency. The easy access to numerous sources of information from the virtual library allows breadth in the projects concerned, besides offering many possibilities for innovative designs.
Project-based learning (PBL) via the integration of technology in science teaching is one of the contextual learning approaches that has gained much popularity and increased attention in the recent years. Project-based activities become the precursor for the advancement of Science and Technology Education (STE) in developing countries. Research findings indicate that the use of technology allows students to present their projects in an interesting and comprehensive manner. Science projects are usually triggered from simple questions or problems in various contexts. With a close guidance by the mentors, students’ project work could provide the motivating and effective contexts for the acquisition of research skills, scientific understanding, problem solving and critical/creative thinking skills. Technology, in a variety of sophisticated forms, in turn challenges the student to create many tasks in line with each individual’s knowledge and proficiency. The easy access to numerous sources of information from the virtual library allows breadth in the projects concerned, besides offering many possibilities for innovative designs. The SAW international programme aims to introduce into science education an increased awareness of the different perspectives, ways of life and national traditions of students in various countries. It raises the awareness of the ways in which science and technology interact with society, industry and the environment. The programme with its suggested topics can be viewed and downloaded from the official website
The SAW international programme aims to introduce into science education an increased awareness of the different perspectives, ways of life and national traditions of students in various countries. It raises the awareness of the ways in which science and technology interact with society, industry and the environment. The programme with its suggested topics can be viewed and downloaded from the official website  The SAW programme focuses on project work upholding the following three main processes of learning, i.e. (a) Individual student’s exploratory work where the student carries out investigations to explore science locally; (b) Compilation of the
The SAW programme focuses on project work upholding the following three main processes of learning, i.e. (a) Individual student’s exploratory work where the student carries out investigations to explore science locally; (b) Compilation of the  SCORM standard is another aspect this project is using. SCORM nowadays become a widely used requirement for e-learning projects. There is still a lot of confusion, especially within the instructional design community, regarding what it is and when it should be used. SCORM or the Sharable Content Object Reference Model provides a common technical framework for the development of reusable instructional objects for computer and Web-based learning. This paper presents the design and implementation of course content development based on mind map approach using SCORM.
SCORM standard is another aspect this project is using. SCORM nowadays become a widely used requirement for e-learning projects. There is still a lot of confusion, especially within the instructional design community, regarding what it is and when it should be used. SCORM or the Sharable Content Object Reference Model provides a common technical framework for the development of reusable instructional objects for computer and Web-based learning. This paper presents the design and implementation of course content development based on mind map approach using SCORM.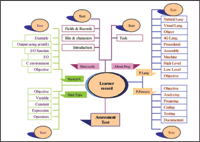 Run time environment describes the LMS responsibility to launch SCOs based requests from the learner and the sequencing rules of the content organization. Therefore, the main requirements in this phase are: to have Application Programme Interface (API), which is a set of functions to achieve the communication between the course content and LMS and facilities to utilise details from manifest file through data model. This data model enables the LMS to track learners’ progress. The steps developed in this phase are as follows:
Run time environment describes the LMS responsibility to launch SCOs based requests from the learner and the sequencing rules of the content organization. Therefore, the main requirements in this phase are: to have Application Programme Interface (API), which is a set of functions to achieve the communication between the course content and LMS and facilities to utilise details from manifest file through data model. This data model enables the LMS to track learners’ progress. The steps developed in this phase are as follows: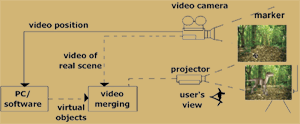 AR has been used in entertainment, military training, medical, engineering design, robotics and tele-robotics, manufacturing and consumer designs for many years prior to its introduction. Fotis Liarokapis, Panos Petridis, Paul Lister and Martin White (2002) have developed “an interactive e-learning AR environ-ment” called Multimedia Augmented Reality Interface for E-Learning (MARIE) in which users can view and interact with 3D virtual objects aided by online instructors. This system uses the head-mounted display, camera, and computer for visual augmented reality to present 3D multimedia information to the learner regardless of gender or age group.
AR has been used in entertainment, military training, medical, engineering design, robotics and tele-robotics, manufacturing and consumer designs for many years prior to its introduction. Fotis Liarokapis, Panos Petridis, Paul Lister and Martin White (2002) have developed “an interactive e-learning AR environ-ment” called Multimedia Augmented Reality Interface for E-Learning (MARIE) in which users can view and interact with 3D virtual objects aided by online instructors. This system uses the head-mounted display, camera, and computer for visual augmented reality to present 3D multimedia information to the learner regardless of gender or age group.  20 students who attended this experimental study were very excited to see the real time augmented scenes in the classroom. They interacted with markers by moving them to different location within the camera view where the virtual models were recognised. In this case, a projector is connected up from the laptop and the whole class gets to view what is displayed. However, the following limitations were found while using this setup in the classroom.
20 students who attended this experimental study were very excited to see the real time augmented scenes in the classroom. They interacted with markers by moving them to different location within the camera view where the virtual models were recognised. In this case, a projector is connected up from the laptop and the whole class gets to view what is displayed. However, the following limitations were found while using this setup in the classroom. 
 Virtual objects were developed in the format of 3D using 3DS Max software. The created 3D models of dinosaurs were converted to
Virtual objects were developed in the format of 3D using 3DS Max software. The created 3D models of dinosaurs were converted to  Qualcomm recently announced the names of the developers who will participate in its Wireless Reach BREW Application Funding Programme. The company has established a fund of $1 million to encourage the creation of BREW-based wireless applications for segments such as education, government, healthcare, public safety and environment.
Qualcomm recently announced the names of the developers who will participate in its Wireless Reach BREW Application Funding Programme. The company has established a fund of $1 million to encourage the creation of BREW-based wireless applications for segments such as education, government, healthcare, public safety and environment. RapideL enables Instructional Designers and SMEs to author AICC/SCORM compliant content from the basic MS-Word authoring interface. RapideL comes with inbuilt robust project management capabilities such as online review mechanisms, issue tracking and the ability to publish web versions. It promotes collaborative development over the network/ Web while also working as a standalone tool without multiple installations. It allows publishing with track changes and support for language localisation.
RapideL enables Instructional Designers and SMEs to author AICC/SCORM compliant content from the basic MS-Word authoring interface. RapideL comes with inbuilt robust project management capabilities such as online review mechanisms, issue tracking and the ability to publish web versions. It promotes collaborative development over the network/ Web while also working as a standalone tool without multiple installations. It allows publishing with track changes and support for language localisation. Microsoft has givenMicrosoft’s Office software to communities across the United Kingdom to help physically and mental disabilities through Microsoft’s annual Community
Microsoft has givenMicrosoft’s Office software to communities across the United Kingdom to help physically and mental disabilities through Microsoft’s annual Community UNESCO has launched a high-priority ‘Initiative on Teacher Training’ in sub-Saharan Africa. This initiative will assist the continent’s 46 sub-Saharan countries in restructuring national teacher policies and teacher education.
UNESCO has launched a high-priority ‘Initiative on Teacher Training’ in sub-Saharan Africa. This initiative will assist the continent’s 46 sub-Saharan countries in restructuring national teacher policies and teacher education. Schools of Ireland will receive a technology boost under the National Development Plan 2007-2013. The new investment is designed to develop an e-learning culture in schools.
Schools of Ireland will receive a technology boost under the National Development Plan 2007-2013. The new investment is designed to develop an e-learning culture in schools. The Patent Office said that prior art cited by the SFLC raised questions about the patent. It was reported earlier that Blackboard had taken legal action against Desire2Learn Inc. This firm has also asked the patent office to re-examine Blackboard’s patent. The re-examination will take two years.
The Patent Office said that prior art cited by the SFLC raised questions about the patent. It was reported earlier that Blackboard had taken legal action against Desire2Learn Inc. This firm has also asked the patent office to re-examine Blackboard’s patent. The re-examination will take two years. Pioneering software that enables children to design their own computer games could significantly improve the teaching of literacy, design and ICT skills in schools. A new project at Heriot-Watt University in United Kingdom aims to produce “Adventure Author”The objective is to show thatcomputer games, as well as being fun, offer a great way of motivating pupils to learn. They can develop their reativity, and in many cases, generate better results than conventional teaching methods. The 27-month research project “Supporting Creativity in Computer Game Authoring” is due to run untilSeptember 2008. Adventure Author will allow 10-14 year olds to design and build 3D, interactive fantasybased computer games, which will involve developing characters, writing dialogue, plot-structuring and visual design, as well as dealing with technical programming issues and testing/evaluating the games.
Pioneering software that enables children to design their own computer games could significantly improve the teaching of literacy, design and ICT skills in schools. A new project at Heriot-Watt University in United Kingdom aims to produce “Adventure Author”The objective is to show thatcomputer games, as well as being fun, offer a great way of motivating pupils to learn. They can develop their reativity, and in many cases, generate better results than conventional teaching methods. The 27-month research project “Supporting Creativity in Computer Game Authoring” is due to run untilSeptember 2008. Adventure Author will allow 10-14 year olds to design and build 3D, interactive fantasybased computer games, which will involve developing characters, writing dialogue, plot-structuring and visual design, as well as dealing with technical programming issues and testing/evaluating the games. China started CPU research and development in 2001, and the first chip, Godson I, came out in September 2002, bringing the country’s microprocessor industry a step closer to the world leading manufacturers in the United States and Japan. China has since developed three more generations of the Godsongenerations of the Godson — Godson II B, Godson II C and Godson II E. The latter models triple the computing speed of the previous ones.
China started CPU research and development in 2001, and the first chip, Godson I, came out in September 2002, bringing the country’s microprocessor industry a step closer to the world leading manufacturers in the United States and Japan. China has since developed three more generations of the Godsongenerations of the Godson — Godson II B, Godson II C and Godson II E. The latter models triple the computing speed of the previous ones.









