bridging this gap. A big investment towards innovation and new indigenized product development is required to cater to Indian markets like retail, insurance etc.
How meaningful have been the domestic market opportunities for you?
Although in our journey so far, we have not focused towards the domestic arket, lately, we have seen a sudden potential for growth of eLearning in India. To tap this potential, Brainvisa has innovated a product called RapideL, a rapid
eLearning tool which has proved to be a boon to the Indian training community. We have also invested in vertical specialisation to tap verticals
like aviation to begin with. There are significant opportunities forinnovating and building products around insurance, retail and manyother booming sectors.
What needs to be done to promote elearningin India?
A huge e-learning funding initiative from the Government could propel the looming domestic talent shortage. This kind of concept prevails in countries like Australia where the Government has budgeted and pays for professional re-skilling. Also, large Indian universities could follow the path of University of Phoenix to again propel good e-learning initiatives. Such large initiatives sually require government or large private funding. Very recently Brainvisa has made a partnership deal to extend the educational services to South African market.
Could you throw some light on how different or similar are the Indian e-learning initiatives and the foreign ones?
Well, our product RapideL has created waves the world over. We have received a large number of enquiries from various parts and hence we have appointed various resellers to provide local presence. We have recently signed up with resellers in UK, Portugal, South Africa, Germany, Italy, Australia, and Switzerland. Our direct custom learning solution services however are focused for the USA, UK, UAE and Australian market where we have our local offices.
Our offices are located close to our customers as it gives us a chance to learn their business problems more like their employee rather like an external vendor, and this enables us to work closely to serve them beyond their equirement.
How do you see the global market for e-learning?
Globally, even today, 25-30% of a company’s training blend is eLearning and the remaining is predominantly Instructor Led Training. Global companies budget 3-4% of an employee’s annual salary for training. With the gradual shift towards elearning in overall training spend, we feel e-learning has a long way to go. Your services cover a diversified sector of the market (K-12, higher education, corporate learning etc).
immerse are your learning solutions for hose markets and which sector do you think will see the maximum growth in next few years? Brainvisa builds and will continue to build learning solutions for all these categories. In my opinion, the category growth is more country specific. Currently, there is a large demand and supply gap in the corporate training market in India. K- 12 and higher education market are lagging but has the potential be the largest growth segment in years to come. In developed economies, corporate training market will continue to grow faster than K12.
What have been the critical roadblocks for you in this sector? Building deeper, integrated partnership with clients take enormous amounts of time in the
industry. Our most critical and the biggest road block has been to try to reduce this time-frame. We can work with a client on any spoke of this wheel to begin with, and would like to transition it towards completing all spokes of this wheel and meet our objective of building a long term partnership. As the CEO
where do you see Brainvisa five years from now?
Size does matter. Five years down, we plan to be one of the most dominant players in the learning industry globally.







 There is a growing tension among majority of the rural students in not being able to cope with the expected level of mastery in certain core subjects like Science, Mathematics and English at the HSC examination levels and also to prepare them for the entrance examination in order to get access to institutes of higher education of some order. “Partnership in Learning'- is an attempt of Annamalai University in Southern India to address this problem statement, the goal of which is to design and develop the ICT based Information Support system to enhance the skill and expertise of High School Students (10+2) in the Tsunami Affected Regions of Cuddalore district. It is intended to deliver science Educational contents based on their curriculum, through various network delivery channels.
There is a growing tension among majority of the rural students in not being able to cope with the expected level of mastery in certain core subjects like Science, Mathematics and English at the HSC examination levels and also to prepare them for the entrance examination in order to get access to institutes of higher education of some order. “Partnership in Learning'- is an attempt of Annamalai University in Southern India to address this problem statement, the goal of which is to design and develop the ICT based Information Support system to enhance the skill and expertise of High School Students (10+2) in the Tsunami Affected Regions of Cuddalore district. It is intended to deliver science Educational contents based on their curriculum, through various network delivery channels. 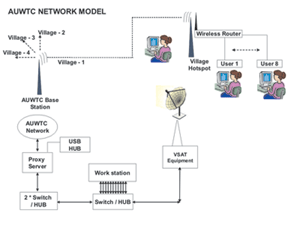 The project aims at building a university centered-village community network that promotes the capacity building, confidence building and the personality development of the rural youth especially the young girl students who have limited opportunity to inte ract with their peer-groups. It will encourage girls to take up Science, Mathematics and technical subjects.
The project aims at building a university centered-village community network that promotes the capacity building, confidence building and the personality development of the rural youth especially the young girl students who have limited opportunity to inte ract with their peer-groups. It will encourage girls to take up Science, Mathematics and technical subjects.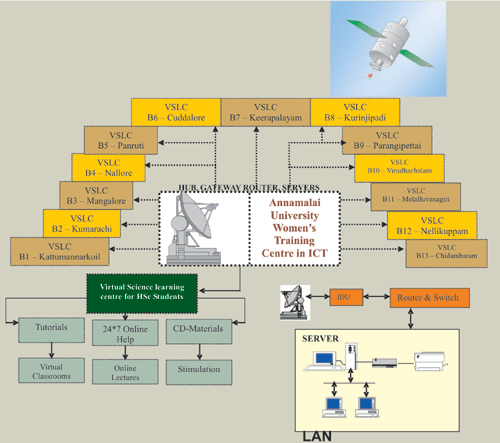 It is proposed to adopt a satellite digital network and cable TV network for the transformation of course materials. A ku-band satellite channel at a speed of 6 Mbps will be established at the Information Technology Training Centre (ITTC) at Annamalai University to ensure real-time course delivery to the local virtual science-learning centres in the selected villages. The courseware also will be transmitted through the local cable TV network. By the end of 2006, it is proposed to establish a minimum of 13 virtual science-learning centres in each blocks. By using a variety of network-based and more traditional distance-education tools, each course involves learners in both independent and group learning activities. Electronic communication occurs between geographically separated learners in using a range of technologies including computer conferencing, audiographic conferencing and web-based delivery. The choice of technology will be based on the subject matter. For instance, application-sharing whiteboards will be preferred to teach Mathematics to show the working of the equations in real-time. Learners at any site can see on their screen what someone at another site writes, and they can also write on, change and augment what has been written by others. The ITTC centre will be fully equipped to provide online teaching, and also online monitoring of the students performance through email. The project identifies three phases: Phase-1 (Pilot Phase) to develop the content, build the partnerships, arrange the availability of the existing delivery channels in one selected village, and perform a proof-of-concept study for the implementation of the computer network link. Phase-2 (Trial Phase) – During this phase, the content and the computer-assisted learning will be introduced into three selected villages. Phase-3 (Roll-out Phase) This stage will master the connecting of individual villages to the learning network.
It is proposed to adopt a satellite digital network and cable TV network for the transformation of course materials. A ku-band satellite channel at a speed of 6 Mbps will be established at the Information Technology Training Centre (ITTC) at Annamalai University to ensure real-time course delivery to the local virtual science-learning centres in the selected villages. The courseware also will be transmitted through the local cable TV network. By the end of 2006, it is proposed to establish a minimum of 13 virtual science-learning centres in each blocks. By using a variety of network-based and more traditional distance-education tools, each course involves learners in both independent and group learning activities. Electronic communication occurs between geographically separated learners in using a range of technologies including computer conferencing, audiographic conferencing and web-based delivery. The choice of technology will be based on the subject matter. For instance, application-sharing whiteboards will be preferred to teach Mathematics to show the working of the equations in real-time. Learners at any site can see on their screen what someone at another site writes, and they can also write on, change and augment what has been written by others. The ITTC centre will be fully equipped to provide online teaching, and also online monitoring of the students performance through email. The project identifies three phases: Phase-1 (Pilot Phase) to develop the content, build the partnerships, arrange the availability of the existing delivery channels in one selected village, and perform a proof-of-concept study for the implementation of the computer network link. Phase-2 (Trial Phase) – During this phase, the content and the computer-assisted learning will be introduced into three selected villages. Phase-3 (Roll-out Phase) This stage will master the connecting of individual villages to the learning network. 








