Govt. works with B-schools for e-Governanace projects
The Department of Information Technology (DIT), Government of India, will receive consultancy services from premier management schools like the Indian Institute of Management, Ahmedabad (IIM-A) and Management Development Institute (MDI), Gurgaon for accessing its e-Governance projects.
The DIT has identified 200 to 300 e-Governance projects for external evaluation, which will include computerisation of land records, registration, income tax, commercial taxes among others. Institutes like IIM-A and MDI, Gurgaon, will be associated in a knowledge partnership and will take up roles of project leaders and validate the DIT's e-Governance projects.
Haryana State Govt. promotes soft skills in schools
Haryana State Government has launched an ambitious programme named, “Development of Soft Skills” for its schools and college students.
This programme is based on EDUSAT platform to provide information about IT and BPO sectors. The government has already invested INR 4.7 million at the school level, while INR 1.5 million is provided for college level students. Initially the scheme has covered 10 schools in each of the eight districts namely Gurgaon, Faridabad, Rewari, Rohtak, Sonipat, Panipat, Panchkula and Ambala.
Chennai engineering college to get digital library
 Chennai based Salem Government College of Engineering, will soon get a digital library to access vast collection of e-resources on various subjects. The library would be subscribed to the Indian National Digital Library in Engineering Sciences and Technology (INDEST), All India Council for Technical Education consortium to get access to the e-resources.
Chennai based Salem Government College of Engineering, will soon get a digital library to access vast collection of e-resources on various subjects. The library would be subscribed to the Indian National Digital Library in Engineering Sciences and Technology (INDEST), All India Council for Technical Education consortium to get access to the e-resources.
The total investment on the project is around INR 2 million. Students would be able to access about 170 online journals through the consortium. The college has already networked the departments functioning in various blocks. The server at the digital library will also be brought into the network, enabling the students to access the resources through computers in their respective departments. A few computers will be installed in the library building also.
Indian students use Internet radio to stay connected
Students at the Indian School of Business, Hyderabad have found a new way to be connected with their faculty and teachers through Internet Radio on the campus.
 The institute is using the local area network (LAN), which has the band-width of 100Mbps in the campus. The total investment to set up a radio station is around INR 55,000 with a personal computer, a headphone and speaker set. Currently, there are more than 50K Radio Stations, which are broadcasting over the Internet. Accor-ding to Bhuvana Ramalingam, Director communication, ISB, e-radio encoura-ges students to exchange information on varied areas, discuss issues and keep everyone informed on the comp-anies, which come to the campus.
The institute is using the local area network (LAN), which has the band-width of 100Mbps in the campus. The total investment to set up a radio station is around INR 55,000 with a personal computer, a headphone and speaker set. Currently, there are more than 50K Radio Stations, which are broadcasting over the Internet. Accor-ding to Bhuvana Ramalingam, Director communication, ISB, e-radio encoura-ges students to exchange information on varied areas, discuss issues and keep everyone informed on the comp-anies, which come to the campus.
IISc, Bangalore offers US$100 laptop for Sakshat portal
The Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore, India has designed a prototype laptop for US$100 for recently launched Sakshat, the one stop portal on education.
IISc Bangalore has come with a prototype design for the laptop that all have in mind that currently costs US$100. Massachusetts Institute of Technology has offered a laptop for US$150 for the Sakshat programme.
Meanwhile, the ministry is planning to create virtual laboratories and a virtual technical university to combat and mainstream the battle to bridge the digital literacy gap. Major institutions, including IIT Delhi, IIT Kharagpur, and IIT Bombay are involved in the project.
IIT Delhi will anchor virtual labs, while IIT Kharagpur will anchor cognitive learning and the virtual technical university and IIT Bombay will provide robotics for this project. IGNOU will provide online courses, while NIOS will offer online-testing on demand.
Read newspaper on mobile phone
Pressmart, a subsidiary of Bodhtree Consulting Limited, and IMImobile, has announced the availability of mPaper, making newspapers available for Indians to read on mobile phones.
 The mPaper technology will enable newsreaders to read and access their favourite newspaper content, while they are traveling also. The mPaper technology also allows user to use features like archives and options to search and save news reports and it would be available on monthly subscription. Pressmart is a new media delivery partner of leading newspapers and magazines published in over 15 languages across 21 countries. IMImobile is a next-generation end-to-end enabler of Mobile Value Added Services (VAS) for mobile operators, media companies and enterprises.
The mPaper technology will enable newsreaders to read and access their favourite newspaper content, while they are traveling also. The mPaper technology also allows user to use features like archives and options to search and save news reports and it would be available on monthly subscription. Pressmart is a new media delivery partner of leading newspapers and magazines published in over 15 languages across 21 countries. IMImobile is a next-generation end-to-end enabler of Mobile Value Added Services (VAS) for mobile operators, media companies and enterprises.
Pressmart will provide mPaper facility in 9 major newspapers of India, including, Hindustan Times (Mumbai and Delhi editions), Deccan Chronicle (Hyderabad and Chennai Editions), DNA, Indian Express, The Asian Age, The Financial Express, The New Indian Express, The Telegraph and Pioneer.
Sarva Shiksha spending on right track!
Spending on the government's flagship elementary education programme, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan at the end of December 2006 accounted for 70% of its annual allocation.
In the first nine months of the current fiscal, nearly INR 10,000 crore of the budgeted INR 13,750 crore has been spent. The Human Resources Development ministry hopes that the good show will result in increased allocation for the forthcoming fiscal. This fiscal, the programme has already utilised 75% of funds available, which is a little over INR 13,000 crore. For the first nine months (April to December) of the last fiscal, the all India spend was 54.2%.
Assam and Orissa, which continue to be areas of concern, have shown an increased utilisation of funds. Tamil Nadu, which had performed poorly in the quarter ending September 30, has improved on its expenditure. It May be recalled that Tamil Nadu, which has traditionally been one of the better performing states, had slowed down due to management problems and local body elections, which meant that funds couldn't be disbursed. From the current year, the Punjab government has taken over the responsibility of paying salaries to teachers. This would mean that a portion of the SSA funds earmarked as teacher salaries would remain unutilised.
The SSA has earmarked the percentage of funds that can be spent on each component-salaries, civil works, etc. For the forthcoming fiscal, the programme will be given INR 8,000 crore, which with a 50:50 ratio would mean that the annual budget for the programme – Centre and state share put together – will be INR 16,000 crore.
IGNOU launches smart card system for Indian students
Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU) is planning to launch a smart card system for Indian students.
 IGNOU will give the smart card system to each student, which will carry information on admission, projects, assignments, attendance, practicals and semester results.The card will help students to keep record on their study activities.
IGNOU will give the smart card system to each student, which will carry information on admission, projects, assignments, attendance, practicals and semester results.The card will help students to keep record on their study activities.
Each student would be issued a
smart card with a unique password, which can be used by specified computers having the software to read the data. IGNOU has
already issued 100 cards on trial basis.
Cambridge College plans to launch e-learning centre in Mumbai
Cambridge College is planning to launch e-learning centre in Mumbai. The college will establish the centre with the association of Indian Universities.
The idea is to provide the opportunity for higher education to the workforce there, plying them with the skills needed to join the ever-growing international business world. The centre will provide education and training in leadership, entrepreneurship, and international trade and practices. 







 There is a growing tension among majority of the rural students in not being able to cope with the expected level of mastery in certain core subjects like Science, Mathematics and English at the HSC examination levels and also to prepare them for the entrance examination in order to get access to institutes of higher education of some order. “Partnership in Learning'- is an attempt of Annamalai University in Southern India to address this problem statement, the goal of which is to design and develop the ICT based Information Support system to enhance the skill and expertise of High School Students (10+2) in the Tsunami Affected Regions of Cuddalore district. It is intended to deliver science Educational contents based on their curriculum, through various network delivery channels.
There is a growing tension among majority of the rural students in not being able to cope with the expected level of mastery in certain core subjects like Science, Mathematics and English at the HSC examination levels and also to prepare them for the entrance examination in order to get access to institutes of higher education of some order. “Partnership in Learning'- is an attempt of Annamalai University in Southern India to address this problem statement, the goal of which is to design and develop the ICT based Information Support system to enhance the skill and expertise of High School Students (10+2) in the Tsunami Affected Regions of Cuddalore district. It is intended to deliver science Educational contents based on their curriculum, through various network delivery channels. 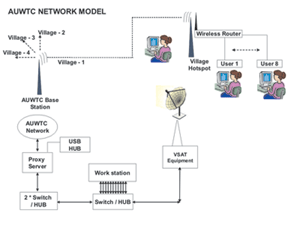 The project aims at building a university centered-village community network that promotes the capacity building, confidence building and the personality development of the rural youth especially the young girl students who have limited opportunity to inte ract with their peer-groups. It will encourage girls to take up Science, Mathematics and technical subjects.
The project aims at building a university centered-village community network that promotes the capacity building, confidence building and the personality development of the rural youth especially the young girl students who have limited opportunity to inte ract with their peer-groups. It will encourage girls to take up Science, Mathematics and technical subjects.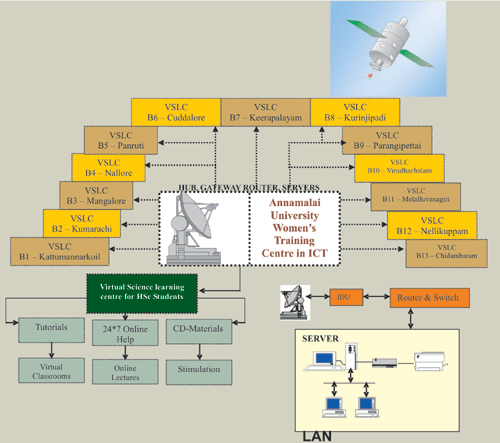 It is proposed to adopt a satellite digital network and cable TV network for the transformation of course materials. A ku-band satellite channel at a speed of 6 Mbps will be established at the Information Technology Training Centre (ITTC) at Annamalai University to ensure real-time course delivery to the local virtual science-learning centres in the selected villages. The courseware also will be transmitted through the local cable TV network. By the end of 2006, it is proposed to establish a minimum of 13 virtual science-learning centres in each blocks. By using a variety of network-based and more traditional distance-education tools, each course involves learners in both independent and group learning activities. Electronic communication occurs between geographically separated learners in using a range of technologies including computer conferencing, audiographic conferencing and web-based delivery. The choice of technology will be based on the subject matter. For instance, application-sharing whiteboards will be preferred to teach Mathematics to show the working of the equations in real-time. Learners at any site can see on their screen what someone at another site writes, and they can also write on, change and augment what has been written by others. The ITTC centre will be fully equipped to provide online teaching, and also online monitoring of the students performance through email. The project identifies three phases: Phase-1 (Pilot Phase) to develop the content, build the partnerships, arrange the availability of the existing delivery channels in one selected village, and perform a proof-of-concept study for the implementation of the computer network link. Phase-2 (Trial Phase) – During this phase, the content and the computer-assisted learning will be introduced into three selected villages. Phase-3 (Roll-out Phase) This stage will master the connecting of individual villages to the learning network.
It is proposed to adopt a satellite digital network and cable TV network for the transformation of course materials. A ku-band satellite channel at a speed of 6 Mbps will be established at the Information Technology Training Centre (ITTC) at Annamalai University to ensure real-time course delivery to the local virtual science-learning centres in the selected villages. The courseware also will be transmitted through the local cable TV network. By the end of 2006, it is proposed to establish a minimum of 13 virtual science-learning centres in each blocks. By using a variety of network-based and more traditional distance-education tools, each course involves learners in both independent and group learning activities. Electronic communication occurs between geographically separated learners in using a range of technologies including computer conferencing, audiographic conferencing and web-based delivery. The choice of technology will be based on the subject matter. For instance, application-sharing whiteboards will be preferred to teach Mathematics to show the working of the equations in real-time. Learners at any site can see on their screen what someone at another site writes, and they can also write on, change and augment what has been written by others. The ITTC centre will be fully equipped to provide online teaching, and also online monitoring of the students performance through email. The project identifies three phases: Phase-1 (Pilot Phase) to develop the content, build the partnerships, arrange the availability of the existing delivery channels in one selected village, and perform a proof-of-concept study for the implementation of the computer network link. Phase-2 (Trial Phase) – During this phase, the content and the computer-assisted learning will be introduced into three selected villages. Phase-3 (Roll-out Phase) This stage will master the connecting of individual villages to the learning network.  SmartChecker is the innovative platform that integrates mobile technologies into teaching and learning environment for the particularly tracking and monitoring of student's class attendance. SmartChecker, exploits the use of personal digital assistance (PDA) to provide mobile and instant graphical display. It also furnishes reports and progress tracks for determining student class attendance baselines, and improves the quality of monitoring and data captured technique, data-driven decision making and school accountability.
SmartChecker is the innovative platform that integrates mobile technologies into teaching and learning environment for the particularly tracking and monitoring of student's class attendance. SmartChecker, exploits the use of personal digital assistance (PDA) to provide mobile and instant graphical display. It also furnishes reports and progress tracks for determining student class attendance baselines, and improves the quality of monitoring and data captured technique, data-driven decision making and school accountability. 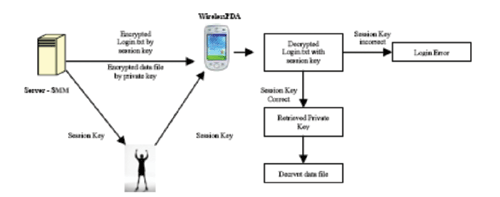
 Due to the inherent data privacy concern, it is important to protect the data in SmartChecker at three levels. (a) Physical security: Protecting the device from loss or theft, and preventing access to the device operating system (OS) and the SmartChecker application if the device does fall into the wrong hands. (b) Data security: Ensuring that if the device does fall into the wrong hands and the OS is accessed, the data stored in the device cannot be accessed. (c) Network security: Preventing eavesdropping during data transmission between the device and the system server. RSA is the most widely used algorithm for public key encryption, and is believed to be secure given sufficiently long keys. Here we modify the classical protocol to take into account of the limitations of hand held devices.
Due to the inherent data privacy concern, it is important to protect the data in SmartChecker at three levels. (a) Physical security: Protecting the device from loss or theft, and preventing access to the device operating system (OS) and the SmartChecker application if the device does fall into the wrong hands. (b) Data security: Ensuring that if the device does fall into the wrong hands and the OS is accessed, the data stored in the device cannot be accessed. (c) Network security: Preventing eavesdropping during data transmission between the device and the system server. RSA is the most widely used algorithm for public key encryption, and is believed to be secure given sufficiently long keys. Here we modify the classical protocol to take into account of the limitations of hand held devices.  Users can simply navigate and hyper-link through different graphs and data points to gain a thorough understanding of each student's class attendances, from the detailed scores, comparison to the average to the overall ranking, perform trend analysis by a set of pre-determined rules.
Users can simply navigate and hyper-link through different graphs and data points to gain a thorough understanding of each student's class attendances, from the detailed scores, comparison to the average to the overall ranking, perform trend analysis by a set of pre-determined rules.  USA Government agencies are giving funds to put video conferencing system in schools. The Rural Development under secretary Thomas Dorr, has given US$25,853,991 funds of 103 distance learning and telemedicine to provide educational and medical services to citizens of 38 states.
USA Government agencies are giving funds to put video conferencing system in schools. The Rural Development under secretary Thomas Dorr, has given US$25,853,991 funds of 103 distance learning and telemedicine to provide educational and medical services to citizens of 38 states.  From Brazil to Pakistan, some of the world's poorest children are to peer across the digital divide in February – reading electronic books, shooting digital video, and chatting with classmates online. Founded by Massachusetts Institute of Technology academics, the non-profit 'One Laptop per Child' project plans to roll out nearly 2,500 of its US$150-laptops to eight nations in the month of February.
From Brazil to Pakistan, some of the world's poorest children are to peer across the digital divide in February – reading electronic books, shooting digital video, and chatting with classmates online. Founded by Massachusetts Institute of Technology academics, the non-profit 'One Laptop per Child' project plans to roll out nearly 2,500 of its US$150-laptops to eight nations in the month of February.  Students are using mobile phones to download english grammar lesson and answer series of multiple choice, true or false questions. Athabasca University, a long-distance post- econdary school, created the cellphone lessons for those wanting to learn english as a second language (ESL). Students from anywhere in world can learn english grammar, through their cell phones.
Students are using mobile phones to download english grammar lesson and answer series of multiple choice, true or false questions. Athabasca University, a long-distance post- econdary school, created the cellphone lessons for those wanting to learn english as a second language (ESL). Students from anywhere in world can learn english grammar, through their cell phones.  Google's research centers outside of the United States typically focus on adapting its products for local markets, but are also involved in developing new offerings and fine-tuning existing ones. Three of its eight research and development centers around the world are in Asia.
Google's research centers outside of the United States typically focus on adapting its products for local markets, but are also involved in developing new offerings and fine-tuning existing ones. Three of its eight research and development centers around the world are in Asia. The representatives were Cikgu Hj Yussof bin Hj Metassim, Sr. Education Officer from the ICT Dept., Ministry of Education, Cikgu Mohd Zamri bin Hj Ismail of Sayyidina Hasan Secondary School and Cikgu Ismail bin Hj Julaihi of PAP Hjh Rashidah Sa'adatul Bolkiah Secondary School.
The representatives were Cikgu Hj Yussof bin Hj Metassim, Sr. Education Officer from the ICT Dept., Ministry of Education, Cikgu Mohd Zamri bin Hj Ismail of Sayyidina Hasan Secondary School and Cikgu Ismail bin Hj Julaihi of PAP Hjh Rashidah Sa'adatul Bolkiah Secondary School. 
 Oracle has launched its online community learning system 'Think.com' to connect schools across Sri-Lanka. Think.com is designed to connect students around the world and engage them in collaborative, project-based learning using technology.
Oracle has launched its online community learning system 'Think.com' to connect schools across Sri-Lanka. Think.com is designed to connect students around the world and engage them in collaborative, project-based learning using technology. Chennai based Salem Government College of Engineering, will soon get a digital library to access vast collection of e-resources on various subjects. The library would be subscribed to the Indian National Digital Library in Engineering Sciences and Technology (INDEST), All India Council for Technical Education consortium to get access to the e-resources.
Chennai based Salem Government College of Engineering, will soon get a digital library to access vast collection of e-resources on various subjects. The library would be subscribed to the Indian National Digital Library in Engineering Sciences and Technology (INDEST), All India Council for Technical Education consortium to get access to the e-resources.  The institute is using the local area network (LAN), which has the band-width of 100Mbps in the campus. The total investment to set up a radio station is around INR 55,000 with a personal computer, a headphone and speaker set. Currently, there are more than 50K Radio Stations, which are broadcasting over the Internet. Accor-ding to Bhuvana Ramalingam, Director communication, ISB, e-radio encoura-ges students to exchange information on varied areas, discuss issues and keep everyone informed on the comp-anies, which come to the campus.
The institute is using the local area network (LAN), which has the band-width of 100Mbps in the campus. The total investment to set up a radio station is around INR 55,000 with a personal computer, a headphone and speaker set. Currently, there are more than 50K Radio Stations, which are broadcasting over the Internet. Accor-ding to Bhuvana Ramalingam, Director communication, ISB, e-radio encoura-ges students to exchange information on varied areas, discuss issues and keep everyone informed on the comp-anies, which come to the campus.  The mPaper technology will enable newsreaders to read and access their favourite newspaper content, while they are traveling also. The mPaper technology also allows user to use features like archives and options to search and save news reports and it would be available on monthly subscription. Pressmart is a new media delivery partner of leading newspapers and magazines published in over 15 languages across 21 countries. IMImobile is a next-generation end-to-end enabler of Mobile Value Added Services (VAS) for mobile operators, media companies and enterprises.
The mPaper technology will enable newsreaders to read and access their favourite newspaper content, while they are traveling also. The mPaper technology also allows user to use features like archives and options to search and save news reports and it would be available on monthly subscription. Pressmart is a new media delivery partner of leading newspapers and magazines published in over 15 languages across 21 countries. IMImobile is a next-generation end-to-end enabler of Mobile Value Added Services (VAS) for mobile operators, media companies and enterprises. IGNOU will give the smart card system to each student, which will carry information on admission, projects, assignments, attendance, practicals and semester results.The card will help students to keep record on their study activities.
IGNOU will give the smart card system to each student, which will carry information on admission, projects, assignments, attendance, practicals and semester results.The card will help students to keep record on their study activities. 











